They first aided humans in the smelting of copper, tin and iron. A ceramic crucible is simply a crucible made from a ceramic material, like kiln-fired clay. Read More…
As a manufacturer and stocking distributor of industrial and technical ceramics, LSP carries the most diversified inventory of ceramic tubes, spacers, bushings, etc. in the industry.
C-Mac International manufactures custom advanced technical ceramic solutions. Our specialties are Zirconia (MgO stabilized and Yttria stabilized), Alumina (90%, 96%, and 99.5% purity), and Tungsten Carbide (Cobalt and Nickel Binder). We also work with steatite, cordierite, silicon nitride, ceramic crucibles, and crushable ceramics. We prioritize customer needs - we have a 48-hour delivery on...
Insaco provides custom grinding and machining services to fabricate precision parts from sapphire, quartz, and most technical ceramics including alumina, zirconia, silicon carbide, silicon nitride, aluminum nitride, and others.
Applied Ceramics is a fabricator of custom-made ceramic parts designed for semiconductor, solar, fuel cell, oil drilling, nuclear, and numerous other industries. Materials include ACI-995 Alumina, Zirconia, and more. Our extensive experience with precision designs supported by our team of specialists ensures that our customers have the ideal solution to meet the needs of their application. To get ...
Aremco is a leader in the custom formulation of advanced industrial materials including technical ceramics. Offering many capabilities for a broad range of machinable & dense ceramic materials, Aremco serves aerospace, automotive, electrical, electronics, heat treating, metallurgical, petrochemical & plastics applications with superior finished ceramic parts. 100’s of standard industrial...

GBC Advanced Materials is a leading provider of advanced ceramic solutions, specializing in a wide range of iso-pressing techniques, green machining, sintering, extrusion, and CNC grinding. With a focus on innovation, precision, and quality, we offer comprehensive capabilities to meet the diverse needs of industries worldwide.
More Ceramic Crucible Manufacturers
Ceramic Crucibles: High-Temperature Solutions for Advanced Material Processing
Ceramic crucibles are essential laboratory and industrial tools, renowned for their chemical and physical stability at high temperatures. These refractory containers are specifically designed for working with substances that require extreme heat, such as metals, alloys, glass, pigments, and various specialty materials. Thanks to their ability to withstand intense thermal environments, ceramic crucibles are indispensable in a wide array of applications, ranging from metallurgy and materials analysis to art and research.
What Is a Ceramic Crucible?
A ceramic crucible is a vessel fabricated from high-performance ceramic materials, chosen for their high melting points, chemical inertness, and mechanical strength under elevated temperatures. Ceramics are nonmetallic, crystalline, inorganic, or amorphous solids that have been processed through firing, cooling, and often glazing. Their surfaces are smooth and relatively inert, which is crucial for preventing unwanted reactions with the substances contained within.
This inertness is critical: if the crucible's surface were reactive, it could contaminate the sample during high-temperature processes. As such, ceramic crucibles are preferred for applications where purity and chemical compatibility are paramount.
Key Features and Benefits of Ceramic Crucibles
- Exceptional Heat Resistance: Ceramic crucibles can sustain temperatures that exceed the capabilities of metal containers, often tolerating conditions above 1,000°C and, in some cases, up to 2,000°C or more.
- Chemical Inertness: The non-reactive nature of ceramics ensures that samples remain uncontaminated, making crucibles ideal for analytical chemistry, precious metal melting, and high-purity material processing.
- Durability: Advanced ceramics are mechanically robust, offering excellent resistance to thermal shock, cracking, and deformation, even after repeated heating and cooling cycles.
- Versatility: Available in numerous shapes and sizes, ceramic crucibles can be tailored to specific industry requirements, supporting diverse applications from laboratory analysis to large-scale metal casting.
- Cost-Effective Solutions: Compared to precious metal crucibles, many ceramic options—such as alumina and silica—are more affordable while still delivering exceptional performance.
Why Choose Ceramic Crucibles Over Alternative Materials?
When selecting a crucible for high-temperature applications, buyers frequently compare ceramics with alternatives such as graphite, quartz, and metallic crucibles (including platinum and steel). Ceramic crucibles generally offer superior thermal and chemical stability, especially for processes involving corrosive fluxes or rapid thermal cycling. For those seeking to optimize operational longevity and minimize contamination risk, high-grade ceramic crucibles often emerge as the preferred choice.
Types of Ceramic Materials Used in Crucibles
A crucial decision in selecting a ceramic crucible involves the choice of base material. The most common ceramic materials used for crucibles include:
- Alumina (Aluminum Oxide): Alumina crucibles are highly popular due to their excellent resistance to both high temperatures and chemical corrosion. They are suitable for applications in metallurgy, glass production, materials research, and analytical laboratories. Alumina crucibles are also cost-effective and widely available in various standard and custom sizes.
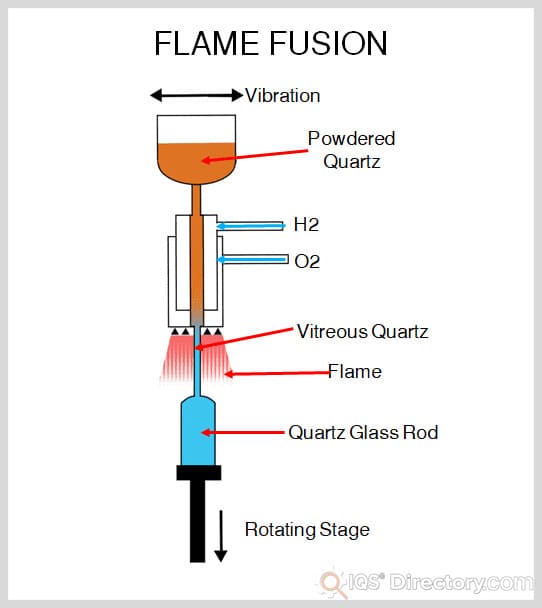
- Silica (Quartz): Silica crucibles are ideal for melting and processing glass and metals with relatively lower melting points. Their high purity and transparency make them suitable for applications requiring optical clarity and minimal contamination.
- Zircon (Zirconia): Crucibles made from zirconia (zirconium dioxide) are favored for their extreme thermal shock resistance and chemical inertness, especially in aggressive environments. These are often used in steelmaking, superalloy production, and specialty chemical processing.
- Spinel: Spinel-based ceramic crucibles combine magnesium and aluminum oxides, offering a balance between thermal stability and mechanical strength. They are often used in advanced ceramics manufacturing and high-temperature chemical reactions.
- Magnesite (Magnesium Oxide): Magnesite crucibles excel in applications involving highly basic or corrosive substances, such as refractory testing, cement analysis, and certain metallurgical operations.
Each ceramic composition reacts differently to heat, pressure, and chemical exposure. It is essential to match the crucible material to the specific process requirements to ensure optimal performance, longevity, and safety.
Common Applications of Ceramic Crucibles
Ceramic crucibles are integral to a wide range of scientific, industrial, and creative fields. Some of the most common applications include:
- Metallurgy: Melting, casting, and alloying metals such as gold, silver, platinum, copper, and steel. Ceramic crucibles are used in foundries, jewelry manufacturing, and metal recycling operations.
- Analytical Chemistry: Performing gravimetric analysis, loss-on-ignition tests, and thermal decomposition studies, where accurate mass measurements are critical.
- Material Science and Engineering: Sintering, calcining, and synthesizing advanced materials, ceramics, and composites at high temperatures.
- Glass Manufacturing: Melting, blending, and refining specialty glasses, enamels, and pigments—where contamination control is essential.
- Research Laboratories: Conducting experiments in earth sciences, solid-state physics, geochemistry, and chemical engineering, often with custom-shaped crucibles for unique research protocols.
- Arts and Crafts: Metalwork, enamel, pigment creation, and pottery, where artists require heat-resistant and chemically stable containers.
Looking for the right ceramic crucible for your application?
Consider these key questions:
- What maximum temperature will your process reach?
- What chemicals or materials will the crucible contact?
- Will you need resistance to rapid heating and cooling (thermal shock)?
- Is contamination control a priority?
- What volume or capacity is required for your process?
- Do you need a standard or custom crucible shape?
- Will the crucible be used in an oxidizing, reducing, or neutral atmosphere?
Design Considerations: How to Select the Best Ceramic Crucible
To maximize the value and performance of your investment, it’s important to understand the various factors that influence ceramic crucible selection:
- Total Capacity: Crucibles are available in capacities ranging from a few milliliters for laboratory use to several liters for industrial furnaces. Select a size that accommodates your sample volume while providing adequate headspace for expansion and stirring.
- Shape and Geometry: Choose from standard forms, such as cylindrical, conical, or rectangular, as well as specialized geometries for unique heating or pouring requirements. The overall shape can impact heat distribution and ease of material removal.
- Wall and Bottom Thickness: Thicker crucible walls can improve durability and resistance to thermal shock but may slow temperature ramp-up. Thin-walled crucibles offer faster heat transfer but may be more susceptible to cracking under mechanical or thermal stress.
- Surface Finish and Glazing: Some crucibles are glazed to further reduce reactivity and enhance cleaning. Consider whether your process benefits from a smooth, nonporous surface.
- Lid and Cover Options: For processes sensitive to atmospheric contamination or requiring controlled heating, crucibles with fitted lids or covers are available.
In addition to these technical specifications, buyers should consider supplier reputation, quality control standards, and available certifications when sourcing ceramic crucibles for laboratory or industrial use.
Modern Manufacturing and Customization
Early ceramic crucibles often featured irregular shapes and inconsistent wall thickness, limiting their performance and refractory capabilities. Modern ceramic crucibles, by contrast, are produced using advanced manufacturing methods such as isostatic pressing, slip casting, and precision machining. These techniques ensure consistent quality, superior refractory properties, and the ability to meet nearly any custom specification.
Manufacturers now routinely offer custom ceramic crucibles engineered for specific processes, including unique shapes, integrated features (such as pouring spouts or handles), and tailored material blends to optimize resistance to corrosion, oxidation, or rapid temperature changes.
Comparing Ceramic Crucibles to Alternative High-Temperature Vessels
When evaluating options for high-temperature containers, it’s helpful to compare ceramic crucibles with other common materials:
- Graphite Crucibles: Excellent for melting non-ferrous metals and alloys, graphite crucibles provide good thermal conductivity but may react with certain chemicals or oxidize at high temperatures.
- Quartz (Fused Silica) Crucibles: Ideal for processes requiring optical clarity and high purity, but with lower mechanical strength compared to most ceramics.
- Metal Crucibles (Platinum, Steel, Nickel): Used for extreme chemical resistance (e.g., platinum) or economic high-volume melting (e.g., steel), but typically more expensive or less refractory than ceramics.
For applications demanding a combination of high-temperature resistance, chemical inertness, and customizable design, ceramic crucibles remain the industry standard.
Industry Use Cases and Buyer Decision Factors
Are you researching suppliers or evaluating which ceramic crucible suits your process? Consider the following real-world use cases and the decision factors that influence purchasing:
- Precious Metal Refining: Jewelers and refiners require crucibles with minimal contamination risk and high temperature stability to ensure purity during gold, silver, and platinum melting.
- Industrial Metal Casting: Foundries choose ceramic crucibles that can handle repeated thermal cycling and exposure to fluxes, enhancing operational lifespan.
- Academic and Government Labs: Researchers often require custom crucible geometries and certified purity levels for advanced material studies, geochemical analysis, and synthetic chemistry.
- Artisanal Glass and Pigment Production: Artists and specialty manufacturers depend on crucibles to create unique glass compositions, colors, and effects that demand both high-temperature stability and inert surfaces.
- Cement and Refractory Testing: Construction materials laboratories use magnesite or alumina crucibles for high-temperature strength and chemical resistance during cement analysis.
When sourcing ceramic crucibles, buyers frequently ask:
- Which ceramic composition offers the best performance for my application?
- How do I balance cost, durability, and contaminant risk?
- What lead times should I expect for standard versus custom crucibles?
- Are there recommended cleaning, handling, and storage practices to extend crucible life?
Frequently Asked Questions About Ceramic Crucibles
- What is the maximum temperature rating for a typical ceramic crucible? Most standard ceramic crucibles can withstand temperatures of 1,500°C to 1,800°C, though specialty materials (like zirconia) may tolerate even higher conditions.
- Can ceramic crucibles be reused? Yes, with proper care and cleaning, ceramic crucibles can be reused multiple times. However, repeated cycling may eventually cause micro-cracking or degradation, especially if used with aggressive chemicals or fluxes.
- How do I clean a ceramic crucible? Cleaning methods depend on the type of residue. Typically, residues can be removed with mechanical brushing, soaking in mild acids or alkalis (compatible with the ceramic), or high-temperature firing to burn off organic matter.
- What safety precautions should I follow? Always handle hot crucibles with appropriate tongs or heat-resistant gloves. Avoid sudden temperature changes (thermal shock) and inspect crucibles regularly for signs of cracking or wear.
- Where can I purchase high-quality ceramic crucibles? Reputable scientific supply companies, ceramic manufacturers, and specialized distributors offer a wide range of standard and custom ceramic crucibles for laboratory and industrial use.
How to Order: Steps for Sourcing the Right Ceramic Crucible
- Define your process requirements, including temperature range, chemical compatibility, and sample volume.
- Identify the optimal ceramic material (alumina, zirconia, magnesite, etc.) for your application.
- Choose the appropriate shape, size, and any necessary accessories (such as lids or pouring spouts).
- Research suppliers and request technical data sheets, material safety information, and product certifications.
- Request samples or prototypes if your process involves unique requirements or custom geometries.
- Place your order with a supplier that demonstrates quality assurance, technical support, and reliable delivery times.
Ready to Find the Perfect Ceramic Crucible?
Whether you’re upgrading laboratory equipment, launching a new manufacturing process, or seeking specialty crucibles for artistic applications, the right ceramic crucible can make a significant difference in quality, productivity, and safety. Leverage the expertise of reputable ceramic crucible manufacturers, and consider your process requirements carefully to ensure optimal results.
Are you still exploring your options? Compare leading suppliers of alumina crucibles and other ceramic crucible types to find the best match for your needs.
Conclusion: Maximizing Performance with the Right Ceramic Crucible
Ceramic crucibles represent the gold standard for high-temperature material processing in laboratories, industrial facilities, and creative studios. Their unique combination of refractory strength, chemical inertness, and customizability supports a wide spectrum of industries and research disciplines. By understanding material options, design considerations, and application-specific requirements, buyers can make informed decisions that lead to better outcomes, higher purity, and longer equipment life.
For more information on ceramic crucibles, including detailed material properties, custom fabrication options, and supplier recommendations, explore our additional resources and product guides.








 Adhesives
Adhesives Alumina Ceramic
Alumina Ceramic Ceramic
Ceramic Glass
Glass Graphite
Graphite Lubricants
Lubricants Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services